Table of Content
How to Create a Trading Plan: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
By Vincent NguyenUpdated 285 days ago
How to Create a Trading Plan
Creating a trading plan is one of the most important steps for every aspiring trader. A well-crafted trading plan acts as a roadmap, guiding you toward logical decisions and helping you avoid impulsive moves.
This guide simplifies the process by breaking down the core elements of a solid trading plan, including consistent strategies, personal risk management rules, and actionable steps for beginners. By defining a clear structure, you can reduce emotional decisions, set investment objectives, and confidently explore various asset classes.
You’ll discover how to choose a trading style, outline strategies, and track progress in a trading journal. With this systematic approach, your trading journey can become more focused, disciplined, and successful.
Why You Need a Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan is more than just a document. It is your personal plan for navigating unpredictable market conditions across a range of markets. Although professional traders often rely on advanced resources, beginners can still benefit from a simple, step-by-step plan. This helps you chart a clear path through different financial markets, whether you trade stocks, forex, or cryptocurrencies.
Creates Clarity in Trading Activity
When you define your trading rules, you gain an organized perspective on each single trade you undertake. You know your entry criteria, target price, and expected timeline before you place an order. This clarity means you can quickly compare real-time trading prices to your planned entry price. That comparison helps you decide if the current market environment is suitable for your trade entry or if you should wait.
Reduces Emotional Decisions
A trading plan acts like a buffer between your emotions and the market. By predefining your exit strategies, position size, and risk-reward ratio, you keep fear or greed from dictating your actions. This approach goes a long way in avoiding revenge trading, which occurs when traders make impulsive moves to recover from bad trades.
Aligns Trading Goals with Reality
Your trading goals might include a specific profit target or a measurable improvement in your trading skills. When these goals are written down, you create a benchmark to review your progress over extended periods. This process helps you examine whether your trading strategy aligns with your actual performance. If results begin to deviate, it’s a clear signal that you might need to adjust your position sizing rules, risk tolerance, or entry criteria.
Serves as a Comprehensive Decision-Making Tool
Your trading plan offers a complete framework that covers different aspects of your approach to trading. It outlines where you place your stop-loss levels, how much capital per trade you are willing to risk, and the best time frames for your style. When you rely on this framework, you transform guesswork into structured planning, and that boosts your chance of long-term success.
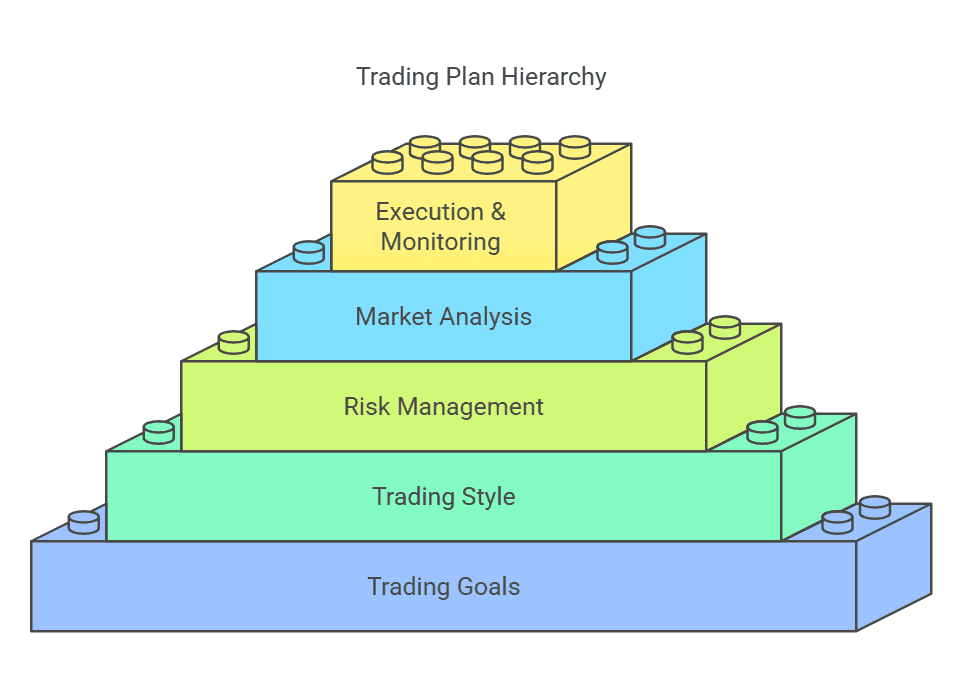
Defining Your Trading Goals and Objectives
Setting precise goals is your initial step toward a successful trading career. These goals guide your actions so you can measure progress more accurately. They also ensure that your trading plan remains aligned with your motivation for trading. If you are unsure why you are trading, you might find it hard to stick to a consistent risk management approach.
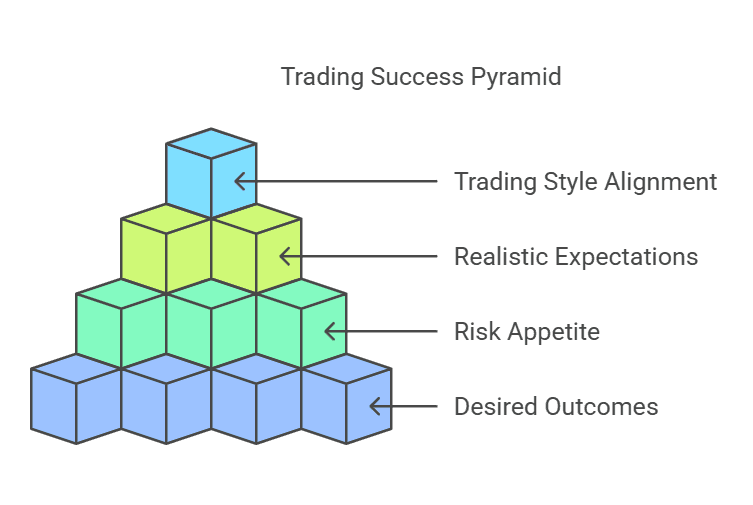
Specify Your Desired Outcomes
Every trade plan begins with defining what you want to achieve. Some traders focus on weekly or monthly profit targets, while others aim to refine certain trading skills. You can choose any objective that drives you, such as improving your swing trading results or mastering a specific technical analysis method. By setting a clear goal, you establish a concrete target that keeps you focused on your trading routine.
Assess Your Risk Appetite
Your attitude towards risk will shape your entire portfolio. Traders with a low risk profile often rely on safer instruments or smaller position sizes. Those with a higher risk tolerance might take on more volatile assets, such as certain forex markets or fast-moving stocks. Clarifying your personal risk management rules prevents you from jumping into trades that exceed your comfort zone. This ensures you approach each opportunity with the right mindset.
Set Realistic Expectations
Many beginners dream of high returns in short periods of time. However, setting unreachable standards can lead to frustration or excessive risk. A better rule of thumb is to choose steady, modest growth that compounds over time. Consider your time commitment and resources. Then, determine what is feasible in your current market. If you plan to open a forex trading plan or a stock trading plan, calculate what a reasonable success rate might be. Stick to that figure as a baseline for monitoring your actual results.
Align Goals with Your Trading Style
A day trader and a swing trader may have different objectives. Day trading often demands concentrated timeframes, while swing trading strategies span multiple days or even weeks. Think about which trading style you prefer, and align your trading goals accordingly. That alignment helps you pick the right time horizon, position size, and target price range for each trade.
Choosing a Trading Style and Strategy
Every successful trading plan grows out of a strategy suited to your personal preferences and the financial markets you follow. Different styles let you address varied market conditions. Some focus on short-term moves, while others aim for medium- to long-term trends. Identifying which type of trader you are helps you select the best approach to trading for your schedule and emotional stamina.
Types of Trading Styles
There is no single approach that works for everyone. Day traders open and close individual trades within the same trading day. This method suits those who thrive on quick decisions and can handle intraday fluctuations. On the other hand, a swing trader holds positions for several days or weeks, aiming to capture shifts in broader market trends. Position traders hold trades for extended periods, basing many decisions on fundamental analysis and longer-term market trends.
Matching Your Style to Your Lifestyle
Your time commitment is a major factor in choosing a trading style. If you have limited time during the trading day, you might opt for swing trading or position trading. But if you can monitor the markets continuously, day trading becomes more feasible. You should also consider your emotional responses. Fast-paced trading can generate stress, while slower approaches may give you more room to breathe and analyze the market in a calm way.
Crafting a Trading Strategy
A trading strategy provides a set of trading rules that outline when and how you enter or exit trades. Some successful traders rely on technical indicators such as support and resistance levels. Others incorporate fundamental analysis to gauge the strength or weakness of particular asset classes. The key is to combine reliable data with your own observations of market conditions. That blend forms a well-rounded trading strategy you can replicate.
Refining Your Approach
You should fine-tune your strategy over time by reviewing your trading journal. That record helps you identify what went right or wrong in each single trade. If you spot a pattern—like consistent losses when you chase a trade or consistent gains when you plan carefully—use that insight to refine your strategy. Over time, these adjustments lead to a more detailed trading plan that aligns with your trading goals and risk appetite.
Risk Management and Position Sizing
Effective risk management is at the heart of every solid trading plan. It ensures that you protect your trading capital by setting clear guidelines for the maximum risk you are willing to accept on any single trade. By defining these boundaries, you reduce the chance of taking on excessive risk that can threaten your entire portfolio.
Personal Risk Management Rules
Begin by clarifying your attitude towards risk. If you have a lower risk tolerance, you might only risk 1% of your trading capital on each position. For traders who can handle more volatility, that figure might rise to 2% or 3%. The key is to set a level that feels manageable while still offering plenty of risk-and-reward opportunities. Once you decide on a percentage for your personal plan, commit to it. This practice prevents you from overexposing yourself, which often happens in emotional decisions or when facing a string of consecutive losses.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Well-placed stop-loss orders are some of the most powerful tools for keeping your losses under control. When you set a stop-loss, you decide on a price level or loss price level at which you will exit if the market moves against you. This technique is often called “risk with stops.” If the trade goes wrong, you have a built-in mechanism that closes the position before your losses grow too large. Stop-losses are crucial in almost every trading style, from day trading to swing trading, because they reduce the risk of a large drawdown.
Determining Position Size
Position sizing rules are another essential component of a comprehensive risk management technique. You calculate your position size based on the difference between your chosen entry price and your stop-loss. Combine this with your overall maximum risk per trade. The result is a carefully calibrated position that aligns with your risk profile and potential gain. For example, if you aim to risk 2% of your account on each single trade, and the distance between your entry criteria and stop-loss is $2, you can determine how many shares or contracts you can open without breaking your own rules.
Balancing the Risk-Reward Ratio
A vital step in risk management is setting a realistic profit target that offers a favorable risk-reward ratio. Many successful traders aim for a ratio of at least 1:2 or 1:3. That means you stand to make two or three times more on winning trades compared to what you lose on the losing trades. Even if you experience several bad trades in a row, a few winners can still keep your trading performance in positive territory. This approach is the cornerstone of profitable strategies in different asset classes, from forex trading to stock trading plans.
Analyzing Market Conditions and Choosing Tools
Market conditions can shift rapidly, so your trading plan must include a clear method for evaluating the current market environment. A consistent approach to market analysis helps you decide whether to enter, hold, or exit a position based on logical trading decisions rather than hunches.
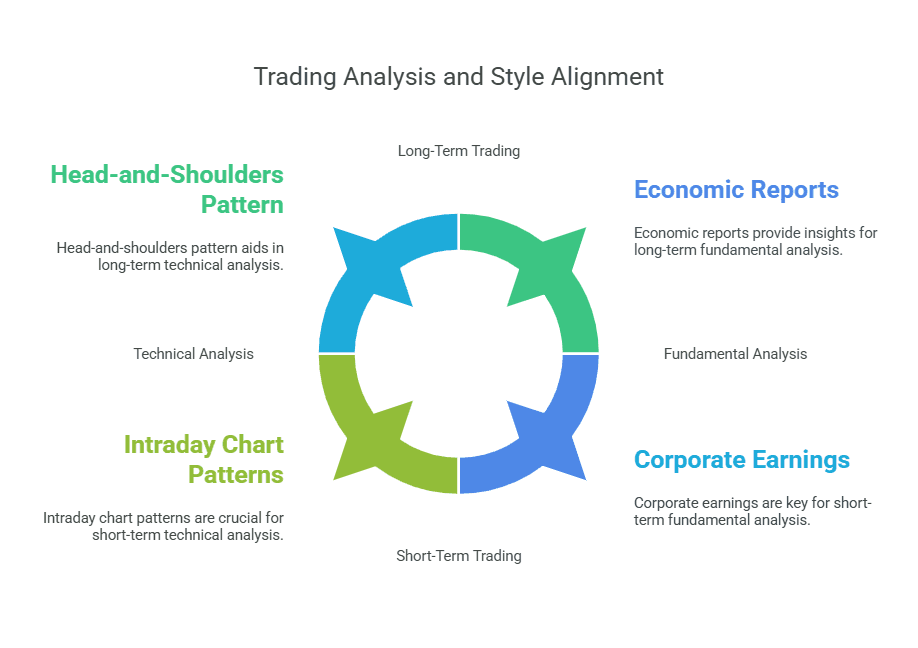
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis relies on price charts and indicators to forecast potential market movements. Many traders watch chart patterns like triangles, head-and-shoulders, or flag chart patterns to identify bullish trading opportunities or bearish setups. You might also look at resistance levels or Fibonacci levels to locate turning points where price action might reverse. Shorter time frames, like the five-minute chart, can help day traders spot intraday signals. Longer time frames, such as a daily chart, may suit a swing trader who prefers holding positions for extended periods.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis examines the underlying value of a security or currency pair. Traders who use this method look at factors such as economic reports, corporate earnings, and global events. They do this to gauge the true worth of a stock or currency pair before entering a trade. By combining fundamental data with chart context, you can form a well-rounded trading strategy that adapts to changing market trends. This is especially helpful in forex trading, where interest rate decisions or macroeconomic indicators can significantly impact major currency pairs.
Selecting Trading Platforms and Tools
Modern trading platforms offer helpful features like real-time charting, advanced order types, and stock screener functionalities. Consider whether a platform provides the market data and charting tools you need for your approach to trading. If you plan to use a specific trading strategy, ensure your chosen platform can accommodate custom indicators or automated strategies. You might also explore how different platforms handle chart patterns, time frames, and advanced analytics so that your strategy remains consistent across different markets.
Matching Analysis to Your Style
Your chosen market analysis method should complement your trading style. For instance, short-term day traders may rely heavily on quick indicators and five-minute charts. Longer-term traders might combine daily chart signals with fundamental analysis. Whatever you choose, make sure it aligns with the time horizon and periods of time you plan to hold a position. Doing so ensures that your market analysis remains relevant, practical, and closely linked to your trading goals.
Practice, Execution, and Monitoring
Practice trading is crucial, especially if you are new to the markets or testing a new strategy. Even professional traders benefit from demo trading or simulated sessions when refining a detailed trading plan. Before risking real money, spend time honing your process under a risk-free environment.
Demo Trading and Practice
Demo trading allows you to place trades using virtual funds. You get to see how your strategy behaves in real market conditions without putting your actual capital per trade at stake. This method works for all sorts of plans, including a forex trading plan, a stock trading plan, or even a futures trading plan. You will learn how to handle trades, set stop-losses, and place orders without incurring the risk of financial loss. This initial step smooths your learning curve and develops essential trading skills.
Monitoring Trades in Real Time
Once you move to real money trading, keep a close eye on each position. Your trade plan should specify how often you will check charts, market trends, or open positions. Frequent reviews help you spot if the market environment has changed drastically, prompting you to adjust your exit criteria or tighten your stop-loss. Day traders might monitor trades moment by moment, while swing traders might review trades once or twice a day. The frequency depends on your time commitment and approach to trading.
Keeping a Trading Journal or Diary
A trading journal is a vital part of tracking your trading journey. Record details about each trade, including entry price, exit rules, position size, and the reason behind your trading decisions. Reflect on emotional responses or market analysis insights that influenced your actions. Over extended periods, you will accumulate enough data to identify recurring mistakes or winning patterns. This helps you refine your strategy and ensures that your trading business remains on a path of continuous improvement.
Evaluating Performance Over Time
Schedule regular reviews of your trading diary to evaluate your trading performance. Look for patterns in profitable trades and examine how they differ from your losing positions. Check if you are adhering to your personal risk management rules. Are you setting realistic goals based on the time frames you trade? If not, make the necessary adjustments. By consistently analyzing your trades, you can fine-tune your strategy, adapt to new market trends, and become more aligned with your overall investment objectives.
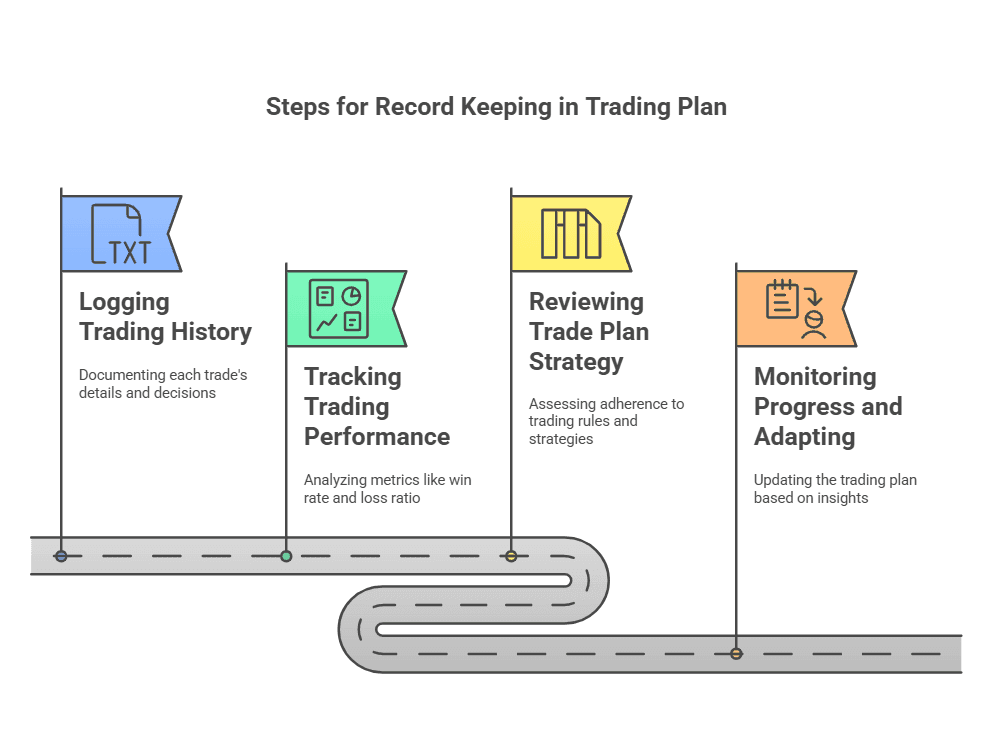
Steps for Record Keeping in Your Trading Plan
Detailed records help you transform scattered trades into a systematic approach. By documenting every aspect of your trading activity, you can identify which tactics lead to success in trading and which ones prompt common trading mistakes.
Logging Your Trading History
One of the first steps for record keeping is to write down each single trade, from the initial step of identifying an ideal trade setup to the exit price. You want to record the time of day, entry criteria, and any relevant chart patterns or fundamental signals. This routine becomes your trading diary, or trading journal, where you store a permanent record of your decisions, emotional responses, and market analysis. Over time, you can detect roadblocks to success or habits that boost your performance.
Tip: Use a spreadsheet or specialized software to make data organization easier.
Tracking Trading Performance
Focus on metrics like your win rate, average gain, and loss ratio. Note how these numbers shift during different market conditions. If you see that your risk-reward ratio drifts out of balance, you may need to adjust your risk management techniques. These evaluations of trade results give you actionable insights. They also help you figure out if your current market approach fits your investment objectives or if you need to explore a different trading style.
Reviewing Your Trade Plan Strategy
Schedule a monthly or quarterly assessment of your trading history. Revisit each single position to confirm whether you followed your trading rules. Ask yourself if your reasons for trading still align with your original investment strategy. Did you take trades that fit your personal plan, or did you deviate under pressure? Spot any patterns of revenge trading or ill-timed trades. These regular reviews ensure you maintain an independence of investment research, so outside noise does not derail your strategy.
Monitoring Progress and Adapting
A well-executed trading plan often requires updates. Market trends shift, and your trading skills grow over time. By examining your detailed records, you can spot moments when your solid trading plan needs a tweak. This might be a new rule for capital per trade, fresh exit strategies, or an adjustment in your daily chart analysis. A trading journal is more than a log; it is a comprehensive decision-making tool that guides you toward a smart plan for future trades.
Monitoring Progress and Adapting
A well-executed trading plan often requires updates. Market trends shift, and your trading skills grow over time. By examining your detailed records, you can spot moments when your solid trading plan needs a tweak. This might be a new rule for capital per trade, fresh exit strategies, or an adjustment in your daily chart analysis. A trading journal is more than a log; it is a comprehensive decision-making tool that guides you toward a smart plan for future trades.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Even a complete trading strategy can fail if you fall into common traps. Many traders struggle with emotional decisions, lack of discipline, or a misunderstanding of inherent risk.
Overtrading and Excessive Risk
Overtrading often happens when traders open multiple positions without a clear strategy, hoping to recover losses or chase quick gains. This behavior leads to taking on plenty of risk. If you exceed your maximum risk allowance on a single position, you jeopardize your entire portfolio. Stick to your consistent risk management approach, and do not open a new trade unless it aligns with your exit criteria, entry price, and position sizing rules.
Ignoring the Market Environment
A trade that works in bullish trading opportunities may fail in a sideways or bearish market environment. Adaptability is key. If the current market looks uncertain, consider placing fewer trades or waiting for a clearer trend to emerge. Day traders might shift to shorter time frames, such as a one-minute time frame or five-minute time frame, to spot quick scalping openings. Swing traders might rely on a 15-minute chart or 60-minute chart to capture broader moves. Align your trading decisions with the chart context you see.
Lack of Clear Exit Rules
Many beginners plan their entry price but forget about exit rules. A well-rounded trading strategy includes both. You should define a profit level that triggers you to close the trade when the market moves in your favor. At the same time, use a stop-loss that limits loss of principal. Without these guards, you risk turning a profitable position into a loss. By setting each exit rule in advance, you avoid emotional responses that lead to holding onto losing trades for extended periods.
Abandoning the Trading Plan
Discipline is the backbone of a successful trading plan. Sometimes, traders abandon their trade plan when they see a sudden market spike or read a piece of hot news. Doing so can lead to impulsive trades that have no foundation in your personal risk management rules. If you feel tempted to deviate, review your trading diary or business plan to remember your reasons for trading. Ask if that move fits your systematic approach or if it is just a knee-jerk reaction.
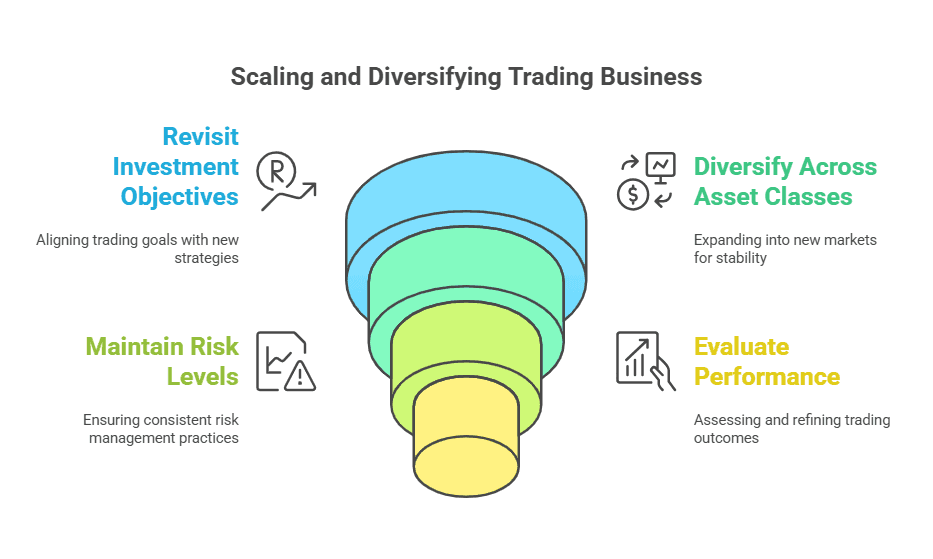
Scaling and Diversifying Your Trading Business
As you gain more confidence and improve your trading skills over time, you may wish to expand your trading business. That can include exploring additional asset classes, deploying new strategies, or increasing your capital allocation. However, scaling up requires the same structured mindset and careful risk assessment.
Revisiting Your Investment Objectives
Before you scale, ask if your investment objectives have changed. Perhaps you have new financial targets or a different time horizon. If so, adjust your trade plan accordingly. Adding new markets or bigger positions without a clear roadmap can lead to confusion. Use your trading history as a guide, noting which approaches have delivered consistent returns. Then, decide how to incorporate those approaches into a larger portfolio allocation.
Diversifying Across Asset Classes
Many experienced traders branch out from stock trading to forex trading or even digital assets. This diversification can safeguard against unexpected downturns in one sector. However, each new market demands its own forex trading plan or futures trading plan. Spend time in a risk-free environment, like demo trading, to familiarize yourself with the nuances of these instruments. Learn their market trends and liquidity patterns, then integrate them into your personal plan as you see fit.
Maintaining Risk Levels
Scaling does not mean you throw your personal risk management rules out the window. Increasing capital per trade or exploring new asset classes should still adhere to your maximum risk parameters. If your strategy calls for risking 2% per trade, you can keep that ratio intact while your account grows. This consistent approach prevents a single trade or a string of bad trades from undoing your progress. It also helps preserve your mental focus as you navigate a broader range of markets.
Evaluating Performance Over Time
Any expansion of your trading game should come with clear metrics for success. Revisit your trading performance more frequently when you are trading new instruments. Check if your updated risk-reward ratio remains profitable, or whether you need new exit rules. Record these developments in your trading diary, noting any lessons you learn. That habit of continuous improvement keeps you aligned with your approach to trading, no matter how large or diverse your portfolio becomes.
Conclusion
A well-structured trading plan is your roadmap to disciplined and successful trading. By setting clear trading goals, defining personal risk management rules, and documenting your trades in a trading journal, you create a system that guides logical decisions and reduces emotional responses. Your plan should align with your trading style, time commitment, and market conditions, allowing for adjustments as you gain experience. Regular evaluation of your performance helps refine your strategy and adapt to evolving markets.
Ultimately, learning how to create a trading plan empowers you to protect your capital, achieve consistency, and build long-term success in the financial markets. With patience and commitment, your plan becomes the foundation of a sustainable trading journey.
Take the first step toward trading success!
Visit TradeSearcher now for expert insights, tools, and resources to craft your perfect trading plan. Start your journey to disciplined and profitable trading today!