Table of Content
BTFD (Buy-The-F*cking-Dip): Meaning, Strategies, and How to Profit
By Vincent NguyenUpdated 390 days ago
Understanding the Power of BTFD in Volatile Markets
The financial markets can seem daunting, especially during periods of heightened volatility. Swings in asset prices can be emotionally and financially taxing. Yet, among experienced traders and investors, there’s a rallying cry that has gained significant traction over the past decade: BTFD, short for “Buy The F*cking Dip.” This phrase encapsulates a strategy that encourages investors to purchase an asset after its price has dropped, assuming it remains fundamentally sound or is still part of a long-term upward trend.
But what exactly does this somewhat irreverent acronym mean in practical terms? Is it really as simple as scooping up an asset whenever it experiences a decline? And are there different ways to implement this approach based on one’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and investing style?
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore all these questions and more. By the end, you’ll not only understand the essence of BTFD but also learn two key strategies you can tailor to your own investment journey. You’ll discover the psychological underpinnings, the potential pitfalls, and how market sentiment can either bolster your returns or leave you in the red.
So, strap in and get ready for a deep dive into one of the most talked-about approaches in modern investing. By the conclusion, you’ll be well-equipped with the knowledge and confidence needed to decide if the BTFD mantra should be part of your personal investment playbook.
What Does BTFD Mean?
BTFD stands for “Buy The F*cking Dip.” Despite its brash tone, the slogan is a simple call to action: whenever there’s a meaningful drop or dip in the price of a stock, cryptocurrency, or any other asset, investors employing this approach aim to capitalize on that lower price by buying more.
While it’s difficult to pinpoint exactly when or where the phrase emerged, it became popular in internet forums and social media platforms like Reddit, Twitter, and financial communities during market downturns particularly when it came to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The premise is to buy an asset “on sale.” If you believe the long-term trajectory of an asset is upward, temporary dips may be seen as excellent buying opportunities to accumulate more shares or tokens at a discount.
This approach is used by both short-term traders looking for swing opportunities and long-term investors who simply see a dip as a momentary setback in an otherwise bullish outlook.
Historical Background of Buying the Dip
The concept of buying the dip far predates the modern-day acronym. Historically, savvy investors like Warren Buffett have championed the idea of buying undervalued assets when they face short-term price declines. During the 2008 financial crisis, for instance, Buffett famously invested in blue-chip companies because he saw their intrinsic values as greater than their temporarily depressed market prices.
With the advent of zero-commission trading and easy-to-use brokerage apps, retail investors have become a powerful force in the markets. The social media era has also led to instant sharing of market trends, news, and opinions. This environment accelerated the popularity of the phrase BTFD, as people rallied each other to hold onto, or even increase, their positions during market dips.
Cryptocurrency markets, known for extreme volatility, latched onto the BTFD ethos. Massive price swings are commonplace in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and various altcoins. Traders and long-term crypto “HODLers” often look at double-digit percentage drops as prime opportunities to accumulate more coins.
Every dip-buying scenario has taught investors a crucial lesson: not every dip is a discount. Some dips are indicative of a longer-term decline, especially if the asset’s fundamentals are deteriorating. Successful BTFD strategies typically require solid research, risk management, and a clear understanding of why a particular asset might rebound.
The Psychology Behind BTFD
Market psychology often boils down to two dominant emotions: fear and greed. When prices drop, fear can lead investors to sell off their holdings, exacerbating the downturn. BTFD exploits this fear by stepping in and buying the asset at a lower price, often driven by the optimistic belief that the market will recover.
When a dip occurs, many investors panic. The BTFD group stands in stark contrast, often urging others to “stay calm and buy more.” This contrarian approach can sometimes pay off if the herd’s fear is unwarranted. However, if the herd’s fear is justified by underlying fundamentals like an unexpected bankruptcy or a macroeconomic shift buying that particular dip can lead to losses.
Another psychological factor is FOMO, where investors feel compelled to buy because they’re afraid of missing a potentially lucrative rebound. BTFD can be fueled by FOMO if people see others bragging about scooping up assets at bargain prices and later boasting about impressive gains.
Investors often search for information that reaffirms their preconceived notions. If you’re convinced that a particular cryptocurrency or stock will soar in value, you might tune out cautionary signals and latch onto any “expert” who says, “Buy The Dip.” Confirmation bias can be dangerous because it blinds you to genuine red flags.
Pros and Cons of BTFD
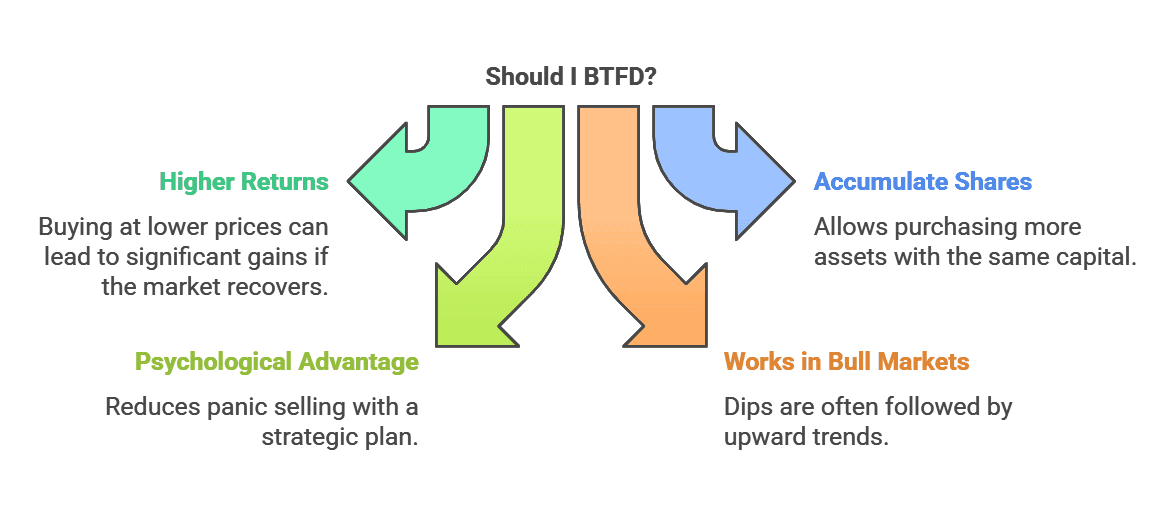
Pros
Potential for Higher Returns
Buying at a lower price can set you up for greater gains if the asset recovers.
Opportunity to Accumulate More Shares
Dips allow you to accumulate more shares or tokens with the same amount of capital.
Psychological Advantage
Having a plan to buy dips can prevent panic selling. You might remain calmer during market corrections knowing you’re positioned to capitalize on lower prices.
Can Work in Bull Markets
In a long-term bull market, short-term dips are often followed by continued upward movement, which validates the BTFD strategy.
Cons
Catching Falling Knives
Sometimes assets continue to drop for fundamental reasons, turning what looks like a “dip” into a sustained downtrend.
Requires Emotional Discipline
In the heat of a market correction, emotions run high. Sticking to a BTFD plan requires discipline and conviction.
Opportunity Cost
If you tie up capital in a declining asset, you might miss out on other investments with better short-term or long-term potential.
Works Best with Research
BTFD is not just a gut feeling. Investors need to validate why an asset is dipping and whether it’s likely to rebound.
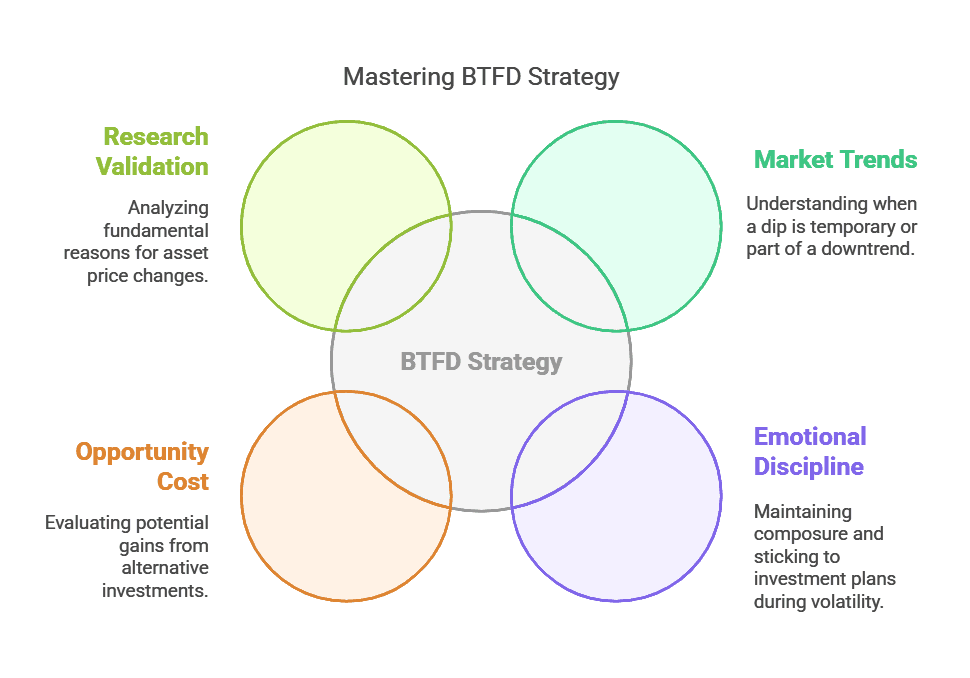
Key Considerations Before You BTFD
1. Fundamental Analysis
- Evaluate a company’s earnings, revenue growth, market share, or a cryptocurrency’s development roadmap and community.
- Ask: Is the asset’s dip due to short-term news, or is there a deeper issue at play?
2. Technical Analysis
- Look at charts, moving averages, and support/resistance levels.
- Identify if a dip has triggered a breakdown of key technical supports or if it’s likely to bounce from them.
3. Your Time Horizon
- Short-term traders may focus on charts and volatility, while long-term investors prioritize fundamentals and macroeconomic trends.
- If your goal is long-term accumulation, a dip might offer a cost-effective entry point.
4. Risk Tolerance
- Only invest money you can afford to lose, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrency.
- If you’re risk-averse, consider scaling into your position gradually rather than going all-in.
5. Market Conditions
- In a bear market, dips can be frequent and deep, requiring a different approach than in a bull market.
- Be mindful of broader economic indicators like interest rates, GDP growth, and geopolitical events that could influence market sentiment.
6. Stop-Loss and Exit Strategy
- Always know your exit plan before entering a trade.
- Set stop-losses to protect against catastrophic losses if the asset keeps falling.
Strategy Example #1: Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) with a BTFD Twist
Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the asset’s price. Over time, this strategy can help you average down your cost basis when prices are declining and potentially benefit from any future rebound.
When combined with the BTFD mentality, you can slightly modify your standard DCA routine to invest a bit more during dips. This approach still offers the discipline and systematic benefits of DCA while giving you a chance to capitalize on lower prices.
Step-by-Step Guide
Determine Your Regular Contribution
- Decide how much you plan to invest every week or month. For example, let’s say you invest $200 every two weeks in a particular index fund or cryptocurrency.
Set a Threshold for “Dips”
- Define what a “dip” means for you. It could be a 5%, 10%, or 20% decline from a recent high.
- Example: If you consider a 10% decline from the monthly high as a dip, you’ll deploy extra capital when this occurs.
Maintain a Cash Reserve
- Keep some money aside specifically for dip-buying opportunities.
- If your typical DCA amount is $200, you might set aside an extra $100 to $200 for days or weeks when the market meets your dip threshold.
Execute Your Base DCA
- Continue investing your $200 every two weeks, no matter what happens in the market.
Deploy Extra Capital on Dips
- If the price of your chosen asset drops by 10%, invest an additional $100 or $200.
- This can help you accumulate more shares at a discounted price, lowering your overall cost basis.
Monitor and Adjust
- Periodically review your performance. If dips are happening frequently, you might need to adjust your thresholds or conserve more cash to make the strategy sustainable.
Sample Scenario
Asset: An S&P 500 index fund trading at $400 per share. Regular DCA: $200 every two weeks (approximately 0.5 shares). Dip Threshold: 10% from the recent high. Market High: The fund trades at $420, then drops to $378 (a 10% decline). Dip Buy: You invest your regular $200 plus an extra $100 you’ve set aside, snagging shares at $378. Result: After the dip, the fund recovers to $400. Your average cost for the shares you purchased in that dip is $378, so you’re already seeing an unrealized gain on that portion of your holdings.
Strategy Example #2: Technical Analysis for Swing Trades
For those more interested in short-term to medium-term gains, swing trading based on technical analysis can be a viable way to execute a BTFD strategy. Rather than setting a strict dollar amount to invest over time, you identify “support levels” or “oversold signals” to pinpoint optimal entry points during dips.
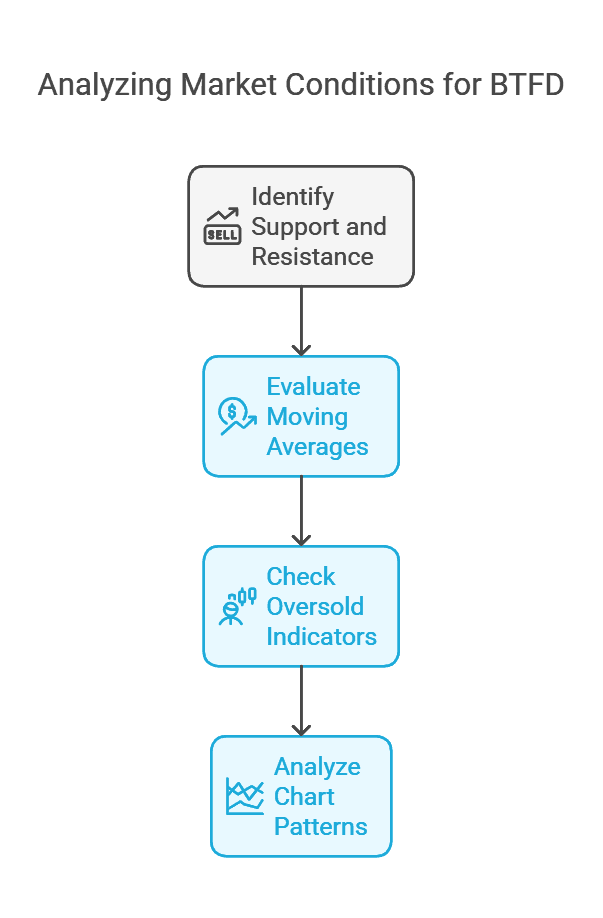
Identifying Support Levels and Trends
Support and Resistance
- A support level is a price at which an asset tends to stop falling, as buyers come in and drive prices higher.
- A resistance level is a price at which an asset tends to stop rising, as sellers come in.
Moving Averages
- Simple Moving Average (SMA) or Exponential Moving Average (EMA) can indicate a trend.
- If a stock is trading above its 50-day and 200-day moving averages, it might still be in a bullish uptrend despite short-term dips.
Oversold Indicators
- Technical tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can signal if an asset is oversold (typically when RSI is below 30).
- Oversold conditions often precede a bounce, making them attractive points to “buy the dip.”
Chart Patterns
- Patterns like double bottoms, ascending triangles, or cup and handle can offer clues about when a dip may reverse.
Sample Scenario
Asset: A tech stock trading at $50, still in a bullish trend over the past six months. Recent High: $60. Price has fallen to $48. Technical Indicators: The RSI is at 28, suggesting oversold conditions. The price is hovering around the 50-day SMA, which has historically acted as support. Entry Point: You decide to buy at $48, setting a stop-loss around $45 to limit risk if the dip continues. Target Price: Based on your analysis, the next significant resistance is around $55. Execution Buy: At $48, expecting a rebound. Stop-Loss: $45, capping your loss at $3 per share if the downward trend continues. Take Profit: $55, locking in a $7 gain per share if the bounce occurs.
Risk Management in BTFD
No matter which strategy you use, whether DCA or swing trading, risk management is paramount. Here are some essential tools and techniques:
1. Stop-Loss Orders
- Automatically sell part or all of your position if the price drops to a preset level.
- Prevents massive losses if a dip turns into a prolonged downtrend.
2. Position Sizing
- Don’t go “all-in” on one trade.
- Use only a fraction of your capital, say 1% to 5% per trade or dip-buying opportunity, depending on your risk tolerance.
3. Diversification
- Spread your investments across different asset classes (stocks, ETFs, crypto, bonds, etc.) and sectors (tech, healthcare, consumer goods, etc.).
- Even the best dip-buying plan can fail if it’s overly concentrated on one asset or sector.
4. Trailing Stops
- If your trade starts to turn profitable, you can move your stop-loss up to lock in gains, while still allowing room for the position to appreciate.
5. Reevaluate Fundamentals
- If the dip is caused by significant bad news like a major lawsuit, accounting fraud, or industry upheaval, revisit your thesis.
- Sometimes the best move is to accept the loss and exit if the long-term outlook has changed drastically.
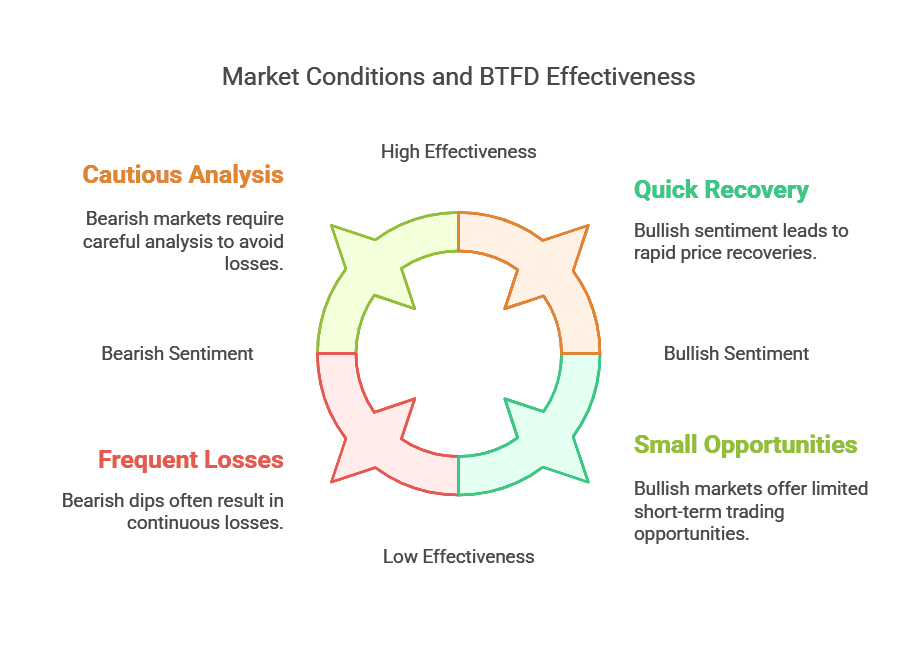
How Market Sentiment Impacts BTFD
Bullish Sentiment
- In a bull market, BTFD works famously well.
- Corrections are often short-lived, and investors who buy dips can ride the wave higher.
- FOMO can drive prices to recover quickly after each dip.
Bearish Sentiment
- In a bear market, the phrase might turn into a grim joke: “Buy The F*cking Dip” can lead to repeated losses if prices keep hitting new lows.
- Technical and fundamental analysis becomes critical to discern a genuine opportunity from a “falling knife.”
Neutral or Choppy Markets
- In sideways markets, dips might be shallow and bounces modest.
- For short-term traders, choppy markets can offer frequent small opportunities. For long-term holders, these periods might not be as fruitful unless combined with other strategies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Buying the Dip
1. Blindly Following Social Media
- Don’t assume every call to BTFD on Twitter or Reddit is grounded in thorough analysis.
- Conduct your own due diligence.
2. Ignoring Fundamentals
- A dip in price may be indicative of deeper financial troubles.
- Always ask why the asset is dipping.
3. No Exit Plan
- Entering a trade or investment without a clear target or stop-loss can lead to emotional decision-making.
4. Over-Leveraging
- Using too much margin or leverage to BTFD can amplify gains but also magnify losses.
5. Panic Selling
- If you buy the dip and the price keeps dropping, panicking could lock in losses that might have been recovered later.
- However, if the fundamentals have changed for the worse, selling may be the prudent choice. The key is to have a plan rather than react out of emotion.
When Not to Buy the Dip
When the Fundamentals Are Deteriorating
- If the company’s quarterly earnings are consistently underperforming or there’s a major scandal, the dip could be justified.
In the Middle of a Broader Economic Crisis
- If the market decline is part of a deep recession or credit crisis, prices can continue to fall for an extended period.
When You Don’t Understand the Asset
- Never invest in something simply because it’s dropping if you don’t fully understand how it generates value or revenue.
When You Can’t Afford to Lose
- If your personal financial situation is fragile, focusing on building an emergency fund may be more prudent than risking capital in volatile markets.
BTFD Across Different Markets
Stocks
Liquidity: Stocks tend to have high liquidity, making it easier to buy and sell quickly. Volatility: Blue-chip stocks usually exhibit less volatility than small-cap or penny stocks. Fundamental Analysis: Earnings reports, P/E ratios, and dividend yields offer insight into a company’s health.
Cryptocurrency
- High Volatility: Price swings can be dramatic, sometimes 10% or 20% in a single day.
- Decentralized Ecosystem: Values can be influenced by technology updates, community sentiment, and regulatory news.
- Risk Management: Essential, given the extreme volatility and lack of long operating histories for many cryptos.
Commodities
- Supply and Demand: Commodities like gold, oil, and agricultural products are deeply affected by global supply-and-demand dynamics and geopolitical events.
- Safe Haven Assets: Precious metals like gold might see price dips less frequently if they’re functioning as a hedge against economic uncertainty.
Forex (Foreign Exchange)
- Macro Influences: Currency pairs are influenced by interest rates, geopolitical events, and economic data releases.
- Leverage: Forex brokers often offer high leverage, so dips can be magnified. Risk management becomes even more critical.
Essential Tools and Resources
Charting Platforms
- TradingView, Thinkorswim, MetaTrader: Provide charts, indicators, and drawing tools.
News Aggregators
- Google Finance, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg: Keep you updated on macro news, earnings reports, and economic calendars.
Social Media and Forums
- Twitter, Reddit (r/Stocks, r/CryptoCurrency): Good for sentiment checks, but always verify the information.
Screeners
- Finviz (for stocks), CoinMarketCap (for crypto): Filter assets based on price changes, volume, and other criteria.
Brokerage Tools
- Many modern brokerages (e.g., Fidelity, Robinhood, Interactive Brokers) offer user-friendly mobile and web apps with built-in research tools.
Conclusion
“Buy The F*cking Dip” is more than just a meme or an internet catchphrase. At its core, it’s a distilled expression of a time-tested principle in investing: seek to buy quality assets at discounted prices. However, as we’ve seen throughout this article, successfully implementing a BTFD strategy requires more than blind optimism:
Research and Analysis
Combine both fundamental and technical analyses to discern whether an asset truly offers value.
Clear Strategy
Whether you choose a systematic DCA approach with a BTFD twist or a more technical swing-trading method, structure is crucial.
Emotional Discipline
The markets can be scary when prices are nosedive. Having a plan helps you avoid panic selling or irrationally going “all-in” at the worst possible moment.
Risk Management
Stop-loss orders, position sizing, and diversification are non-negotiable. Never risk more than you can afford to lose.
Adaptability
Market conditions change. A dip in a bull market may not behave the same way as a dip in a bear market. Stay flexible and be willing to pivot if new information emerges.
When executed thoughtfully, buying the dip can be a powerful tool in your investment arsenal. It can help you accumulate assets at favorable prices and potentially amplify your returns. Yet it’s crucial to remember that not every dip is worth buying. Understanding why the asset is dipping, using strategic methodologies, and maintaining strong risk management practices separate successful BTFD investors from those who become cautionary tales.
So, is BTFD right for you? That depends on your goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook. If you’re confident in the long-term prospects of your chosen assets and have the emotional fortitude to hold through turbulence, then “Buy The F*cking Dip” may very well become your battle cry. If you prefer a more measured, conservative approach, you can still glean value from the underlying principle: buy quality assets at attractive valuations just do it in a way that aligns with your personal financial blueprint.
Ready to put these BTFD insights into action?
At Tradesearcher, we provide real-time analytics, market research, and personalized alerts so you can confidently capitalize on every dip.